
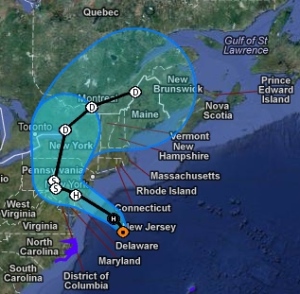
Map showing the evacuation zone around Indian Point Energy Center by the NRDC (via Riverkeeper).
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission will hold a public meeting tonight (Thursday, May 17) on the safety and future of the Indian Point Energy Center (IPEC), a nuclear power plant located in Buchanan, NY, less than 40 miles north of New York City. The Tarrytown, NY “open house” (as it is billed) is designed to explain and answer questions about the annual assessment of safety at IPEC delivered by the NRC in March, but will also serve as a forum where the community can express its concerns in advance of the regulator’s formal relicensing hearings for Indian Point, expected to start later this year.
And if you are in the area–even as far downwind as New York City–you can attend (more on this at the end of the post).
Why might you want to come between Entergy, the current owner of Indian Point, and a shiny new 20-year license extension? As the poets say, let me count the ways:
Indian Point has experienced a series of accidents and “unusual events” since its start that have often placed it on a list of the nation’s worst nuclear power plants. Its structure came into question within months of opening; it has flooded with 100,000 gallons of Hudson River water; it has belched hundreds of thousands of gallons of radioactive steam in the last 12 years; its spent fuel pools have leaked radioactive tritium, strontium 90 and nickel 63 into the Hudson and into groundwater; and IPEC has had a string of transformer fires and explosions, affecting safety systems and spilling massive amounts of oil into the Hudson.
That poor, poor Hudson River. Indian Point sits on its banks because it needs the water for cooling, but beyond the radioactive leaks and the oil, the water intake system likely kills nearly a billion aquatic organisms a year. And the overheated exhaust water is taking its toll on the river, as well.
Indian Point is located in a seismically precarious place, right on top of the intersection of the Stamford-Peekskill and Ramapo fault lines. The NRC’s 2010 seismic review places IPEC at the top of the list of reactors most at risk for earthquake damage.
Entergy was also late in providing the full allotment of new warning sirens within the 10-mile evacuation zone, which is a kind of “insult to injury” shortfall, since both nuclear power activists and advocates agree that Indian Point’s evacuation plan, even within the laughably limited “Plume Exposure Pathway Emergency Planning Zone,” is more fantasy than reality.
With this kind of legacy, and all of these ongoing problems, it would seem, especially in a world informed by the continuing Fukushima disaster, that the NRC’s discretionary right to refuse a new operating license for Indian Point would be the better part of valor. But the NRC rarely bathes itself in such glory.
Instead, when the nuclear industry meets rules with which it cannot comply, the answer has usually been for the regulatory agencies to just change the rules.
Such was the case the night before the-night-before-Christmas, when the NRC and the Federal Emergency Management Agency quietly changed long-standing emergency planning requirements:
Without fanfare, the nation’s nuclear power regulators have overhauled community emergency planning for the first time in more than three decades, requiring fewer exercises for major accidents and recommending that fewer people be evacuated right away.
Nuclear watchdogs voiced surprise and dismay over the quietly adopted revamp — the first since the program began after Three Mile Island in 1979. Several said they were unaware of the changes until now, though they took effect in December.
At least four years in the works, the changes appear to clash with more recent lessons of last year’s reactor crisis in Japan. A mandate that local responders always run practice exercises for a radiation release has been eliminated — a move viewed as downright bizarre by some emergency planners.
The scope of the changes is rivaled only by the secrecy in which they were implemented. There were no news releases regarding the overhaul from either FEMA or the NRC in December or January. Industry watchdogs, such as the Nuclear Information and Resource Service, only learned about the new rules when questioned by the Associated Press.
It was the AP that published an in-depth investigation of lax nuclear regulation last June, and it was the AP that spotted this latest gift to the nuclear industry:
The latest changes, especially relaxed exercise plans for 50-mile emergency zones, are being flayed by some local planners and activists who say the widespread contamination in Japan from last year’s Fukushima nuclear accident screams out for stronger planning in the United States, not weaker rules.
FEMA officials say the revised standards introduce more variability into planning exercises and will help keep responders on their toes. The nuclear power industry has praised the changes on similar grounds.
Onsite security forces at nuclear power plants have practiced defending against make-believe assaults since 1991 and increased the frequency of these drills after the 2001 terrorist attacks. The new exercises for community responders took years to consider and adopt with prolonged industry and government consultations that led to repeated drafts. The NRC made many changes requested by the industry in copious comments.
Naturally.
But, if a nearby resident or a city official were to express concerns about a nuclear plant’s emergency preparedness–like, say, those that live and work around Indian Point–regulators would likely dismiss them as alarmist:
None of the revisions has been questioned more than the new requirement that some planning exercises incorporate a reassuring premise: that little or no harmful radiation is released. Federal regulators say that conducting a wider variety of accident scenarios makes the exercises less predictable.
However, many state and local emergency officials say such exercises make no sense in a program designed to protect the population from radiation released by a nuclear accident.
“We have the real business of protecting public health to do if we’re not needed at an exercise,” Texas radiation-monitoring specialist Robert Free wrote bluntly to federal regulators when they broached the idea. “Not to mention the waste of public monies.”
Environmental and anti-nuclear activists also scoffed. “You need to be practicing for a worst case, rather than a nonevent,” said nuclear policy analyst Jim Riccio of the group Greenpeace.
From the perspective of the industry-captured regulators, if you can’t handle the truth, rewrite the truth. And if there were any doubt about the motives of the nuclear industry, itself, when it comes to these new rules, a reading of the AP report makes it clear: from top to bottom, the revisions require less of nuclear operators.
While officials stress the importance of limiting radioactive releases, the revisions also favor limiting initial evacuations, even in a severe accident. Under the previous standard, people within two miles would be immediately evacuated, along with everyone five miles downwind. Now, in a large quick release of radioactivity, emergency personnel would concentrate first on evacuating people only within two miles. Others would be told to stay put and wait for a possible evacuation order later.
This rule change feels ludicrous in the wake of Fukushima, where a 12-mile radius is assumed to be a no-go zone for a generation, and the State Department advised US citizens to evacuate beyond 50 miles, but it is especially chilling in the context of Indian Point. The stated reasoning behind the tiny evacuation zone is that anything broader would be impossible to execute quickly, so better to have folks just “hunker down.”
“They’re saying, ‘If there’s no way to evacuate, then we won’t,'” Phillip Musegaas, a lawyer with the environmental group Riverkeeper, said of the stronger emphasis on taking shelter at home. The group is challenging relicensing of Indian Point.
Over 17 million people live within 50 miles of IPEC. In February, environmental and anti-nuclear groups asked the NRC to expand evacuation planning to 25 miles from the current 10, and to push readiness zones out to 100 miles, up from 50. They also asked for emergency planners to take into account multiple disasters, like those experienced last year in Japan.
That might have been an opportune time for the regulators to explain that they had already changed the rules–two months earlier–and that they had not made them stronger, they had made them weaker. Not only will the 10 and 50-mile zones remain as they are, the drills for the 50-mile emergency will be required only once every eight years–up from the current six-year cycle.
With the turnover in elected officials and municipal employees being what it is–especially in times of constricting local budgets–even a run-through every six years seems inadequate. An eight-year lag is criminal. (Perhaps the NRC can revise assumptions so that disasters only happen within a year or two of a readiness drill.)
But an extra two years between drills is cheaper. So is the concentration of the evacuation zone in case of quick radiation release. So are many of the other changes. At a time when regulators should look at Japan and ask “What more can we do?” they instead are falling over themselves to do less.
And the nuclear industry needs all the help it can get.
The fact is that without this kind of help–without the weakened rules and limp enforcement, without the accelerated construction and licensing arrangements, without the federal loan guarantees and liability caps, and without the cooperation and expenditures of state and local governments–nuclear could not exist. Indeed, it would not exist, because without this wellspring of corporate welfare, nuclear power plants would never turn a profit for their owners.
In fact, with the cost of new plant construction escalating by the minute (the new AP1000 reactors approved for Georgia’s Plant Vogtle this February are already $900 million over budget), the strategy of energy giants like Entergy rests more on buying up old reactors and spending the bare minimum to keep them running while they apply for license extensions. This is the game plan for Indian Point. It is also Entergy’s plan for Vermont Yankee, a plant granted a license extension by the NRC in March, over the objections of the state government.
The case of Vermont Yankee is currently before a federal appeals court–and New York has filed an amicus brief on Vermont’s behalf, since New York Governor Andrew Cuomo would like to see Indian Point shuttered at the end of its current license, and it knows the NRC has never met a license extension it didn’t like.
Meanwhile, however, Entergy continues to hemorrhage money. The second largest nuclear power provider in the nation posted a first quarter loss of $151.7 million–its stock is down 13% this year–directly as a result of its creaky, inefficient, often offline nuclear reactors. It needs quick, cheap, easy relicensing for facilities like Indian Point if it is ever going to turn things around.
Although maybe not even then. Take, for example, the current plight of California’s San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station (SONGS). San Onofre’s two reactors have been offline since the end of January, when a radiation leak led to the discovery of accelerated wear in over 1,300 copper tubes used to move radioactive water to and from the plant’s recently replaced steam generators:
[Southern California] Edison finished installation of the $671-million steam generators less than two years ago, promising customers they would create major energy savings. Now, officials estimate it will cost as much as $65 million to fix the problems and tens of millions more to replace the lost power.
Both those figures are likely low. No one has yet isolated the exact cause of the wear, though attention focuses on excessive vibration (and that vibration will likely be linked to faulty design and the attempt to retrofit off-the-shelf parts on the cheap), and the time it will take to correct the problem, make repairs and get the reactors up to something close to full power is somewhere between unpredictable and never.
Indeed, Edison is instead talking about running SONGS at reduced capacity, at least for several months. Plant engineers say they believe running the reactors at lower power will minimize vibration (though critics point out this will not resolve the problems with already badly worn tubing), but the reality is much simpler. Every kilowatt the nuclear plant can manage to generate is one kilowatt that Edison won’t have to buy from someone else. There is some warranty coverage for the new generators, but there is none for the replacement costs of the electricity.
Edison will, of course, ask the California Public Utility Commission if it can pass replacement costs on to consumers, but that, in turn, begs another question. When the PUC approved the cost of replacing the steam generators, they did so with the assumption that SONGS would average 88% capacity until its license expires in 2022.
An analysis at the time showed that a one-year outage or a scenario in which the plant would run at lower capacity for an extended period could make the project a money loser. But the PUC found those scenarios to be unlikely and determined that the project would probably be a good deal for ratepayers.
“If the plant runs at 50 to 80 percent capacity for the rest of its life, the entire cost-effectiveness analysis is turned on its head,” said Matthew Freedman, attorney for advocacy group The Utility Reform Network.
Sound familiar?
Regulators, be they at the federal NRC or a state’s PUC, can re-imagine reality all they want, but reality turns out to be stubborn. . . and, it seems, costly.
And don’t think that the industry hasn’t already cottoned to this.
In the midst of a battle over extending the 40-year licenses of two Entergy Corp. nuclear plants near New York City, federal regulators are looking into whether such plants would be eligible for yet another extension.
That would mean the Indian Point plants and others around the county might still be running after reaching 60 years of age.
Bill Dean, a regional administrator for the Nuclear Regulatory Commission, said Wednesday the agency “is currently looking at research that might be needed to determine whether there could be extensions even beyond” the current 60-year limit for licenses.
Yes, the article attributes the initiative to federal regulators, but it strains credulity to believe they came up with this idea on their own. The industry can do the money math–hell, it’s pretty much the only thing they do–extending a license for 40 years beyond design life has got to be more profitable than extending a license for only 20 years.
And let’s be clear about that. The design life of Generation II reactors–the BWRs and PWRs that make up the US nuclear power fleet–is 30 to 40 years. When the plans were drawn up for Indian Point, Vermont Yankee, San Onofre, or any of the other 98 reactors still more-or-less functioning around the country, the assumption was that they would be decommissioned after about four decades. Current relicensing gives these aged reactors another 20 years, but it now turns out that this is only an interim move, designed to buy time to rewrite the regulations and give reactors a full second life. Eighty years in total.
It is yet another example of how rules are shaped–and ignored–to protect the bottom line of the nuclear industry, and not the safety of US citizens. (Or, for that matter, the pocketbooks of US consumers.)
And so, it is yet another example of why the Nuclear Regulatory Commission cannot be allowed to continue its rubberstamp relicensing.
And this is where you come in: As mentioned at the top, the NRC’s Bill Dean (the same guy looking into doubling the license extensions) will be in Tarrytown, NY, along with other government and Entergy representatives to answer questions and listen to testimony about the past, present, and future of Indian Point.
The open house is from 6 to 8 PM, and the public meeting is from 7 to 9 PM at the DoubleTree Hotel Tarrytown, 255 South Broadway, Tarrytown, NY.
Riverkeeper, in coordination with Clearwater, NYPIRG, Citizens’ Awareness Network, Occupy Wall Street Environmental Working Group, IPSEC, Shut Down Indian Point Now, and others will be holding a press conference before the open house, at 5:30 PM.
If you live in New York City, Riverkeeper is sponsoring busses to Tarrytown. Busses leave at 3:45 PM sharp from Grand Central (busses will be waiting at 45th St. and Vanderbilt Ave.). More info from SDIPN here. Reserve a place on a bus through Riverkeeper here.






You must be logged in to post a comment.